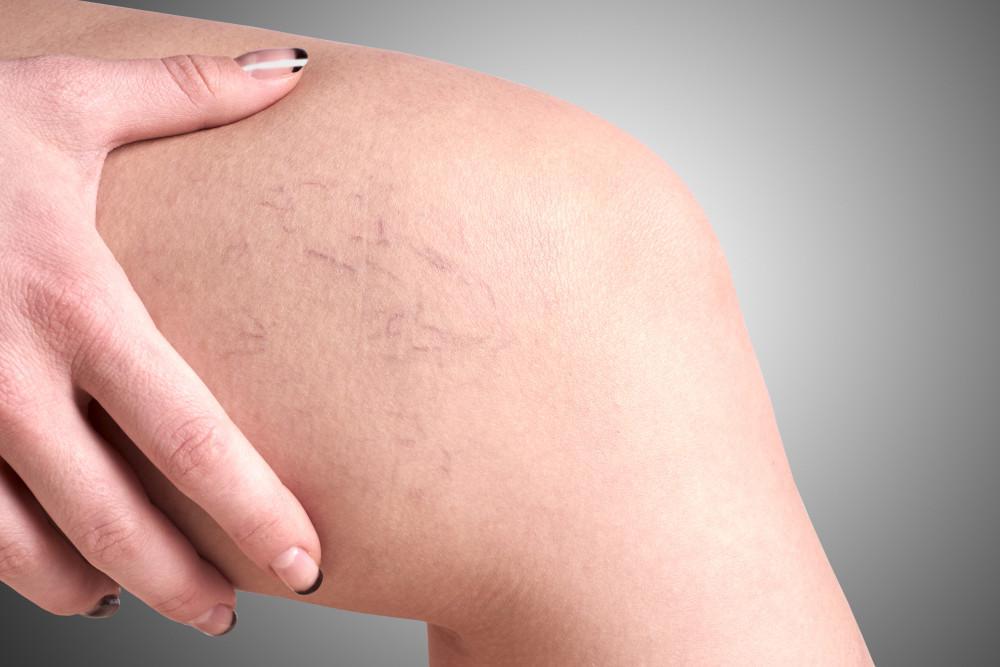
Varicose and spider veins can happen to anyone at any age, but mostly, it affects pregnant women and older people. Varices are a very common phenomenon. Many studies claim that around 10 to 15 percent of men and older women have varicose or spider veins. Genetics also plays a major role here.
Other risk factors are as follows:
- a sedentary lifestyle
- weight gain
- prolonged standing
- pregnancy.
Causes
The causes of varicose veins are not exactly known. In many cases, it is because of the weakness or absence of the valves in veins that cause poor venous circulation. Valves normally act to make sure that the blood doesn’t flow backwards, away from the deep veins and the heart. They are located in perforating veins and a few deep veins. In many cases, vein walls weaken because of the pooling of the blood. The walls become weaker, letting the volume of blood increase, hence causing varicose veins.
They are caused by diseases like:
- phlebitis (inflammation of the veins)
- blood clots
- any obstruction to blood flow in the veins
- congenital abnormalities of the veins.
Symptoms
Many people who have varicose veins see no physical symptoms. But, they may be concerned over the cosmetic look of varicose veins.
The symptoms may include:
- aching
- cramping
- itching
- swelling
- fatigue
- A dull ache
- pressure sensation from varicose veins.
More severe symptoms of varicose veins are:
- bleeding
- thrombophlebitis or blood clot within the varicose vein
- skin ulceration
- weeping oozing dermatitis
- stasis dermatitis.
In severe cases, the skin may turn fibrotic and scarred and forms an inverted hourglass look. Always consult a doctor when suffering from varicose veins.
Treatments
There are ways to treat varicose veins. It varies based on the location and size of the veins, symptoms, and skin changes, if any.

The potential treatments are:
- leg elevation while sitting or sleeping.
- compression dressings with single or multilayered systems.
- compression stockings.
- sclerotherapy.
- ablation (destruction) of abnormal veins with laser, radiofrequency or other methods.
- surgery (removal of the varicose veins, like “phlebectomy” or vein stripping)
Sclerotherapy and laser therapy help in treating spider veins or telangiectasias, while surgery and ablation are ideal for treating larger varicose veins. To know more, visit the website.